Acidification Effects on PEM Fuel Cell Efficiency

Introduction
Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFCs) have emerged as a promising technology for clean energy generation. These fuel cells utilize a proton-conducting membrane to facilitate the electrochemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen, producing electricity, heat, and water as byproducts.
However, one significant challenge that impacts the efficiency and longevity of PEMFCs is the acidity of the medium within the cell. In this article, we will explore the effects of acidity on PEMFC efficiency and discuss how certain components can contribute to acidification. Furthermore, we will introduce Venair Group, a leading company specializing in materials for PEMFC hoses designed to mitigate acidification issues.

The Impact of Acidity on PEMFC Efficiency
Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM):
The heart of a PEMFC is the proton exchange membrane, which conducts protons while blocking the flow of electrons. The acidity of the medium directly affects the performance of the membrane. An excessively acidic environment can lead to membrane degradation, reduced proton conductivity, and ultimately, decreased fuel cell efficiency.
Catalyst Activity:
Acidic conditions can adversely affect the catalysts used in PEMFCs, particularly on the anode side where hydrogen oxidation occurs. These catalysts become less active in an acidic environment, resulting in slower electrochemical reactions and decreased power output.
Durability:
PEMFCs are expected to have long operational lifetimes, but high acidity levels can accelerate the degradation of various components, leading to reduced durability and increased maintenance costs.
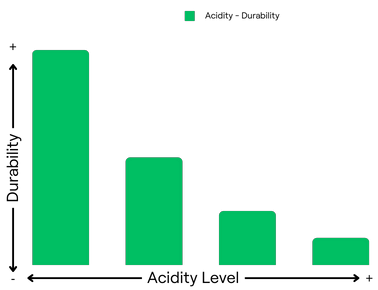
Materials and Acidification
Leachables and Volatiles:
Acidification of the PEMFC medium can be attributed to the presence of leachables and volatiles from various components within the cell. These can include materials used in gaskets, seals, and hoses, among others. When these materials release acidic substances, it exacerbates the acidity problem.
Fuel Contaminants:
Impurities in the hydrogen fuel supply, such as sulfur compounds, can also contribute to acidification. These contaminants react with the cell components, releasing acidic species that further degrade the PEMFC's efficiency.
Venair Group's Solution
Venair Group is a renowned company that specializes in formulating and developing materials specifically for hoses on the anode side of PEMFCs. Their focus on creating materials that do not contribute to acidification in the medium sets them apart as a leader in the field.
Venair's flexible hoses are designed to meet the stringent requirements of various high-tech industries, including BioTech, BioPharm, aerospace, and, notably, Fuel Cell technology.
Key Advantages of Venair Group's Materials:
Acid-Resistant:
Venair's materials are carefully formulated to resist acidification, ensuring that they do not release acidic substances into the PEMFC medium. This promotes the long-term efficiency and durability of the fuel cell.
High-Quality Manufacturing:
Venair Group prides itself on precision manufacturing, which results in hoses that meet the highest industry standards. This reliability is crucial for industries where safety and performance are paramount.
Sustainable Solutions:
As the world moves towards a greener future, Venair's commitment to clean energy technologies like PEMFCs aligns with global sustainability goals.
Conclusion
Acidification of the medium is a significant challenge in the operation of PEM Fuel Cells, affecting efficiency, durability, and overall performance. The contribution of leachables, volatiles, and fuel contaminants to acidification cannot be overlooked. Venair Group stands out as a leader in the industry, offering materials and hoses specifically designed to mitigate these acidification issues. By providing acid-resistant components, Venair Group plays a vital role in advancing PEMFC technology and supporting a sustainable energy future.