First electrification, next sustainability

The global landscape of energy consumption has undergone a profound transformation over the years, marked by the relentless rise in demand for electricity. In this comprehensive exploration, we will dissect the intricate evolution of electrification, detailing how energy demands have surged, and electricity has become the cornerstone of the transition to a cleaner and more sustainable energy future.
What percentage of the current energy system can be electrified?
In January 2022, electricity held a pivotal but nuanced role in the global energy landscape, constituting approximately 20% of the world's final energy consumption. This figure, however, is subject to variations contingent upon the diverse array of sources and methodologies employed for its calculation, in addition to the specific year of reference.

It underscores the multifaceted nature of electrification, where the metrics defining its current impact remain sensitive to measurement intricacies and contextual considerations.
As we contemplate the trajectory towards a more electrified world, a broad estimation places the potential reach of electrification within the range of 50% to 70% of the global energy demand.
This approximation, while indicative of a significant electrification potential, demands careful regional scrutiny and consideration of specific conditions. Regional disparities, technological advancements yet to unfold, and dynamic policy shifts are pivotal factors that can sway the capacity for electrification across various sectors.
Acknowledging this fluidity is crucial as we envision the future landscape of electrification, a dynamic journey influenced by evolving technologies and the responsive adaptability of global energy policies.
The Surge in Electricity Demand:
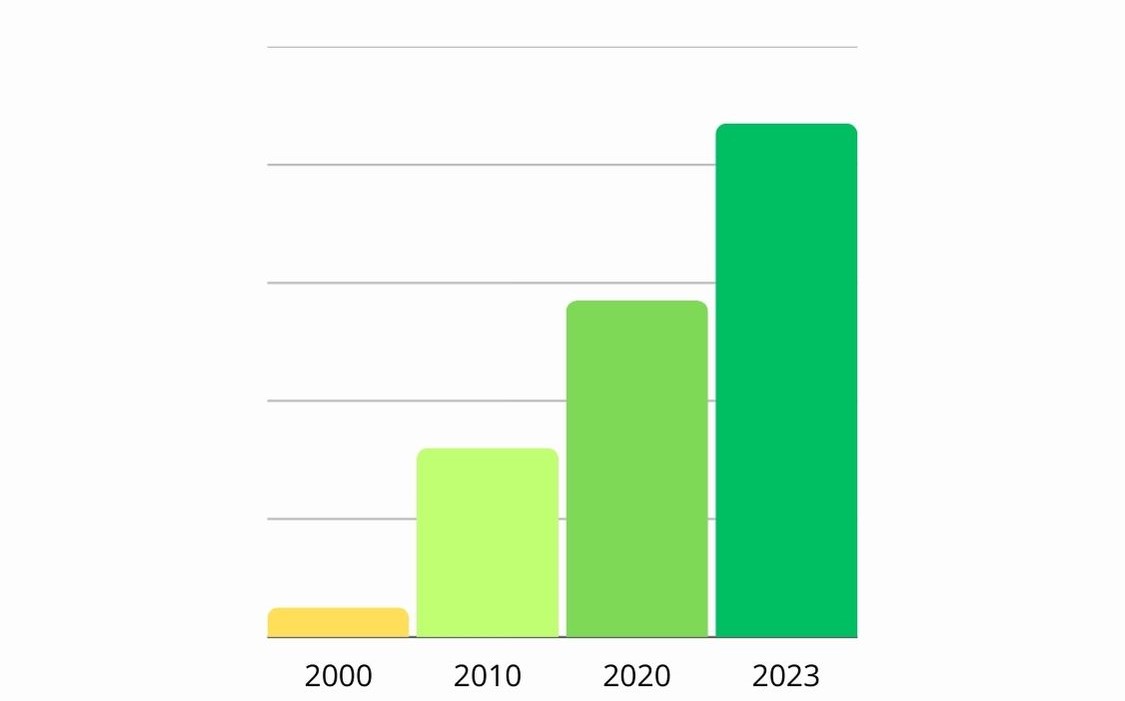
- 2000-2010: The first decade of the 21st century witnessed a notable surge in global electricity demand. From 2000 to 2010, the demand increased by approximately 27%, driven by urbanization, industrialization, and the proliferation of electronic devices.
- 2010-2020: The subsequent decade saw an even more accelerated pace, with electricity demand surging by nearly 25%. The digitization of economies, widespread electrification of appliances, and the growing need for reliable power in developing nations were key contributors.
- 2020-2030: Projections suggest that by 2030, global electricity demand could rise by another 30%, primarily fueled by the electrification of transportation, heating, and industrial processes.
The Evolving Energy Mix:
To meet the escalating demand for electricity, the global energy mix has undergone a significant shift, with an increasing emphasis on cleaner and renewable sources.
Renewable Energy:
- 2000-2010: In 2000, renewable energy sources contributed around 13% to the global electricity generation mix. By 2010, this share had increased to approximately 20%, driven by advancements in solar and wind technologies.
- 2010-2020: The next decade witnessed a remarkable surge, with renewables constituting nearly 29% of the global energy mix by 2020. Solar and wind energy, in particular, experienced unprecedented growth.

- 2020-2030: Projections indicate a continued upward trajectory, with renewables anticipated to reach a 40% share in the global electricity mix by 2030, marking a pivotal step towards a cleaner energy future.
Fossil Fuels:
- 2000-2010: At the turn of the century, fossil fuels dominated the energy landscape, contributing approximately 64% to global electricity generation. Despite concerns about environmental impact, this share only slightly decreased to 62% by 2010.
- 2010-2020: The subsequent decade marked a more noticeable decline in reliance on fossil fuels, with their share dropping to around 56% by 2020. Increased awareness of climate change and policy measures contributed to this shift.
- 2020-2030: Projections suggest a further decline, with fossil fuels expected to constitute around 50% of the global electricity mix by 2030, underscoring the ongoing transition to cleaner alternatives.

The Imperative of Electrification:
The surge in electricity demand is intricately linked to the imperative of electrification. Sectors that traditionally relied on other forms of energy, such as transportation and industrial processes, are now poised for a profound shift towards electricity.
Transportation Electrification:
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): In 2020, EVs accounted for approximately 4% of global vehicle sales. Projections indicate that by 2030, EVs could constitute over 30% of the total market share, representing a paradigm shift towards cleaner transportation.
Industrial Electrification:
Process Heating: Currently, only about 10% of industrial heating processes are electrified. Expanding electrification in industries, particularly through advanced electric heating technologies, could significantly reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
The Road Ahead:
The surge in electricity demand and the shift towards a cleaner energy mix signal a transformative era in global energy dynamics. Electrification stands as the linchpin for achieving sustainability goals, particularly in sectors historically dependent on non-renewable sources. As we navigate this electrified future, the imperative is clear: to foster a transition to a cleaner, more sustainable energy landscape, electrification must permeate industries, transportation, and our daily lives.






