Fatigue analysis in flexible hoses
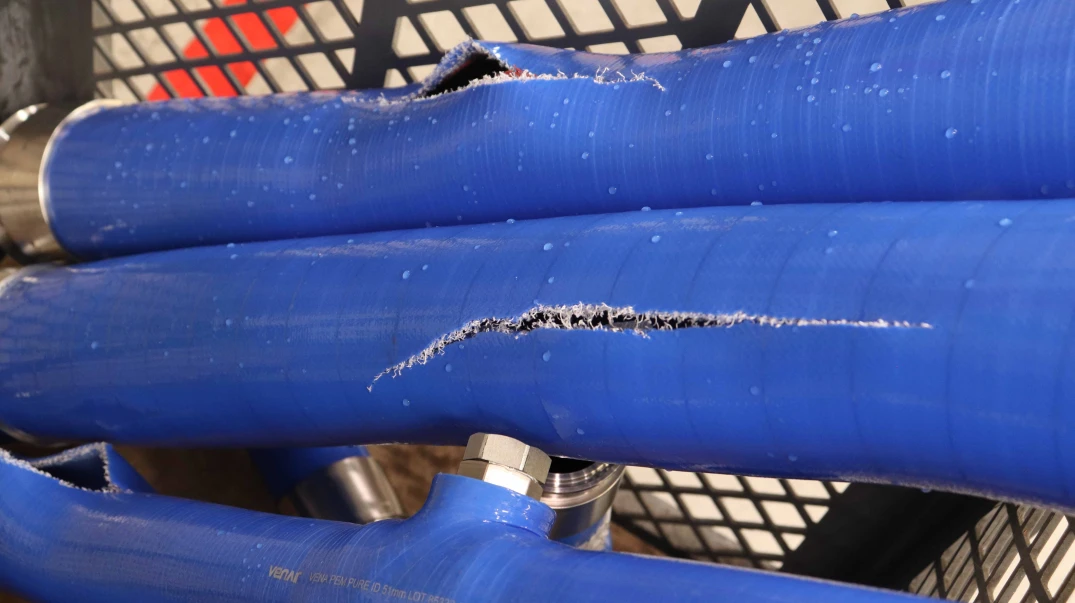

The fatigue analysis is a very important process in the design and engineering of hoses, specially in those applications where the hoses are submitted to cyclic charges along time.
What is the fatigue?
The fatigue is a phenomenon in which a material experience damage or fracture when it’s submitted to repetitive charges, even if these charges are below the resistance limit of the material.
This, makes this phenomenon a very important thing to consider when designing and proposing a hose construction for a specific application. Based on this, elements like fabric reinforcement, wire spring, etc, are included in the constructions to improve their behavior against fatigue due to pressure cycles, compression, or tensile cycles, etc.
Also, changes in the formulation or the materials can be made to withstand the harsh conditions of the target industry. Making the hose more resistant to abrasion, heat, etc, ensuring that hoses are designed to resist the cyclic charges and have an adequate service life is crucial for the security and integrity of the systems in which they are used.
Venair, as an specialize engineering company in transfer solutions based on innovation and customization, has the capability to test all his hoses and materials and evaluate fatigue under real application conditions. To offer customers quality and safe products.
Venair’s Capability
In order to increase the information provided to our customers and offer secure solutions to the market, Venair has strategically invested in nourishing its R&D lab with specific machinery to evaluate the resistance of its products under real conditions.

Today, Venair´s capacity in this sense extends to the following:
-
Steam circuit: saturated steam circulation inside the hose. Evaluate the effect of humidity and high temperature to the hose. Capability to modify test conditions.
-
Possibility to dosage certain chemicals into the circuit to replicate CIP cleaning processes.
-
Pulsator: Mechanical fatigue evaluation by combining pressure, chemical and temperature degradation in hose prototypes. Possibility to test hoses with air including oil particles to replicate engine working.
-
Peristaltic pumps: capability to test useful life of tubing or compatibility under pumping applications at different pressures or RPMs. Different diameters can be tested thanks to interchangeable heads.
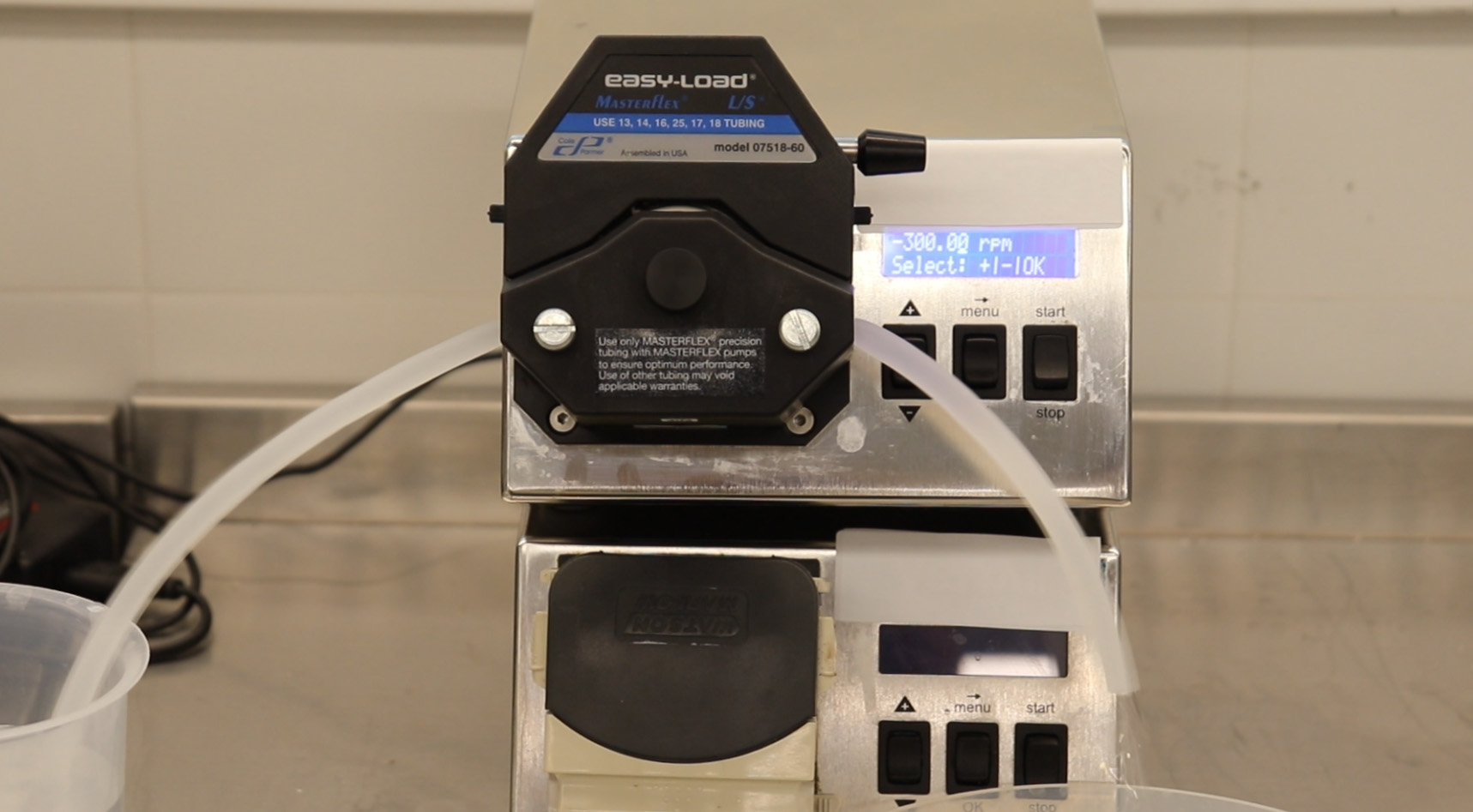

-
Chemical testing machine: chemical transfer circuit for hose fatigue. Capability to test the chemical compatibility of our hoses at different concentrations, pressure, flow and temperatures, and evaluate the degradation under different conditions.
-
Hydrostatic testing machine: to evaluate the hydrostatic pressure resistance of hoses. Also, the variations on the working pressure and bursting pressure due to degradation. Complementary machine to quantify the degradation after fatigue in other machinery.
-
Vibration machines: to make compression and tensile cycles. Also shear and bending stresses in hose prototypes Hot air circuit: hot air circulation. To evaluate the effect of temperature and exposure time to the mechanical properties of the hose. Test capability up to +300°C (572°F).
Conclusions
All this machinery mentioned and capacity, together with the material testing capabilities, allows Venair to offer products based on key features such as security, durability, design efficiency, sustainability, innovation, damage prevention and operational security optimization.
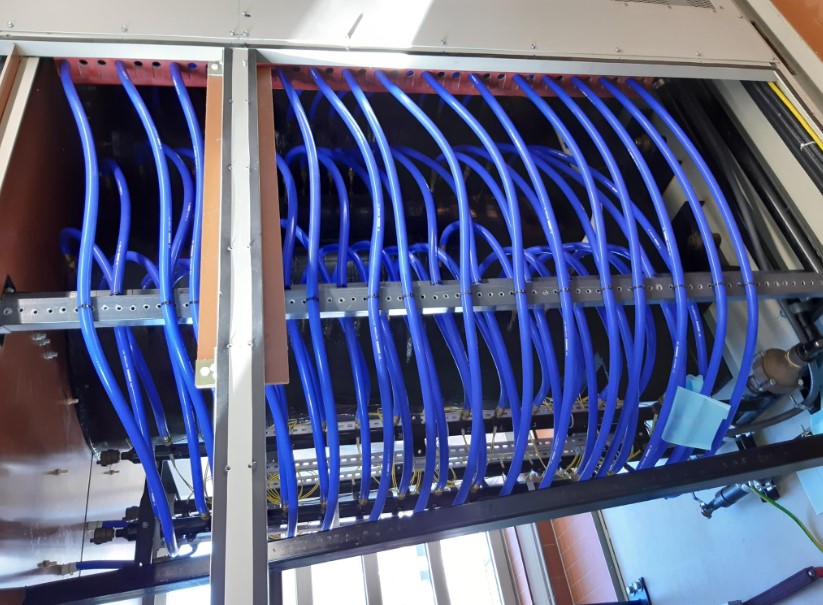

Also, this equipment leads us to adapt our hoses to certain normative compliance thanks to the test capability that in many cases allows us to replicate the official tests needed for certain applications / sectors. Prior to official certification.






