The health hazards of nitrosamine contaminants in consumer products
What are the Nitrosamines and why are dangerous for human health?
Nitrosamines or N-nitrosamines are a wide group of chemical substances that contain an N-nitro group (R2N-N=O). They are considered dangerous for human health as they are probable human carcinogenic and mutation-inducing substances, capable of inducing cancer in diverse organs and tissues including brain, liver, kidney, bladder, etc. For this reason, the majority of N-nitrosamines are classified in groups 2A (Probably carcinogenic to humans) or 2B (Possibly carcinogenic to humans) by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) and as class one impurities (known mutagenic carcinogenics) by the ICH M7(R1) guideline (1).
Despite not having industrial applications, N-nitrosamines are frequently encountered in a variety of end-consumer products as a result of the production processes. Preformed exogenous nitrosamine can be found mainly in processed meats, alcoholic beverages, cosmetics, and other products that are known to carry significant amounts of these harmful substances.
Where can we find the Nitrosamines?
A primary concern surrounding N-nitrosamines is that, besides being incorporated directly, they can also be endogenously generated in the human body from different precursors. Many nitrites and nitrates easily found in food products can transform into nitrosamines when they react with specific amines under biological conditions. For example, they can be formed in the mouth or stomach due to the low pH of this environment. Drinking water can also carry nitrosamines due to the disinfection with dichloramine.
Furthermore, certain precursors of N-nitrosamines can also migrate from plastic and rubber components employed in the manufacturing of consumer goods. For instance, specific compounds utilized as accelerators during the rubber vulcanization process, such as dithiocarbamates and thiurams, have the potential to generate secondary amines as byproducts. These secondary amines can subsequently undergo reactions with existing nitrite or nitrate compounds, resulting in the formation of nitrosamines or nitrosamine precursors, also referred to as nitrosables (2,3). This highlights an additional route through which these hazardous compounds can find their way into various products.
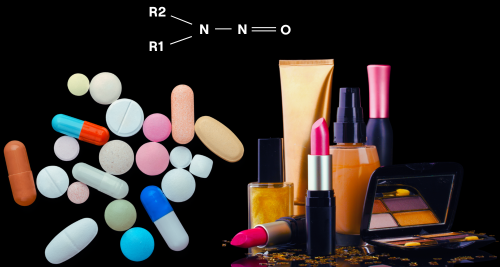
In addition to their presence in food, cosmetic, and various end-user products, there is a significant level of apprehension regarding the existence of nitrosamine compounds in pharmaceuticals intended for human use. In 2018, a series of nitrosamine impurities, primarily N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA), were identified in a class of antihypertensive medications referred to as "sartans." (4) This revelation prompted heightened regulatory oversight, compelling companies to establish effective control strategies in order to prevent or minimize the occurrence of nitrosamine impurities.
Given these concerns, it becomes evident why suppliers operating in the healthcare, cosmetic, and food industries are gradually moving away from production methods that could potentially result in nitrosamine or nitrosatable contaminations in the final products. This transition not only showcases an enhanced commitment to the well-being and health of customers but also acknowledges the necessity of tackling the previously mentioned challenges associated with the presence of nitrosamines.
Venair offers nitrosable-free solutions
Venair's biopharmaceutical, nutrition, and self-care catalog offers a diverse range of silicone-based tubing and products designed for processing materials across various sectors with a high level of safety. These products ensure that harmful compounds such as N-nitrosamines are not present in significant quantities, preventing potential leaching into conveyed materials and subsequent health issues for end-consumers.
We exclusively use nitrosamine and nitrosatable-free raw materials sourced from trusted and accredited suppliers and we employ qualified production processes that ensure that none of our silicon-based products incorporate hazardous substances.
- ICH M7 Assessment and control of DNA reactive (mutagenic) impurities in pharmaceuticals to limit potential carcinogenic risk - Scientific guideline
- Kühne, F., Kappenstein, O., Straßgútl, S., Weese, F., Weyer, J., Pfaff, K. and Luch, A. (2018). N-nitrosamines migration from food contact materials into food simulants: analysis and quantification by means of HPLC-APCI-MS/ MS. Food Additives and Contaminants: Part A, 35 (4), pp 792-805.
- Sung, J.H., Kwak, I.S., Park, S.K., Kim, H.I., Lim, H.S., Park, H.J. and Kim, S.H. (2010). Liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry determination of N-nitrosamines released from rubber or elastomer teats and soothers. Food Additives and Contaminants: Part A, 27 (12), pp: 1745-1754.
- Monteiro, M. A., de Lima, P. C., Novotny, T. S., Santana, D. S., Lima, M. E. D., Dantas, A. S. C. L., ... & de Mendonça Ochs, S. (2023). Investigation of Carcinogenic Impurities of N-Nitrosamines in Sartan Pharmaceutical Products Marketed in Brazil: Development and Validation of Method Based on High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 112(5), 1305-1314.






